Table of Contents
 Hybrid Electric Vehicle
Hybrid Electric Vehicle
Hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) combine an internal combustion engine with one or more electric motors that draw electricity from batteries to operate. High fuel efficiency and minimal tailpipe emissions are combined with the range and power of conventional vehicles in HEVs.
There are currently several different hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) models available. Despite the fact that hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) are frequently more expensive than comparably equipped conventional vehicles, certain costs may be offset by fuel savings or government subsidies https://afdc.energy.gov/vehicles/how-do-hybrid-electric-cars-work
Using the (HEVs)”Can a Hybrid Save Me Money?”
feature on FuelEconomy.gov, you may side-by-side compare HEV and non-hybrid cars. The tool estimates the fuel cost savings associated with the HEV option by comparing the costs of a chosen HEV with a non-hybrid model from the same manufacturer that is comparably equipped.

Using (HEVs) an electric motor to assist
The additional power the electric motor provides in a HEV might enable a smaller combustion engine. Additionally, the battery can decrease excessive engine idling when the car is stopped and power auxiliary loads. These features work together to improve fuel efficiency without compromising performance.

Brake Regeneration (HEVs)
To charge the battery, a hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) cannot plug into off-board sources of power. Instead, the vehicle charges by internal combustion engine and regenerative braking. By employing the electric motor as a generator and storing the acquired energy in the battery, the vehicle is able to recover energy that would otherwise be lost while braking.
(HEVs) Design of Fuel-Efficient Systems
complete hybrids can be created in either series or parallel topologies, and hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) can be either mild or complete hybrids.
Mild hybrids, also known as micro hybrids, employ an electric motor and battery to help power the car. They also have the option of turning off the engine when the car comes to a halt (at a stoplight or in stop-and-go traffic, for example), which increases fuel efficiency. Mild hybrid systems are unable to run the car on just electricity. Although these cars typically cost less than complete hybrids, they don’t offer as much of a fuel-saving advantage.
Full hybrid vehicles can travel short distances and at low speeds thanks to their larger batteries and more potent electric motors. These cars are more expensive than mild hybrids, but they offer better benefits for fuel economy.
The engine and electric motor’s combined power can be combined in a variety of ways. The most popular HEV design, parallel hybrids use mechanical connection to link the engine and electric motor to the wheels. Direct wheel drive is provided by both the internal combustion engine and the electric motor.
WORKING PROCESS OF HYBRID ELECTRIC VEHICLE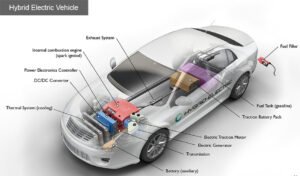
An internal combustion engine and one or more electric motors, which utilize energy stored in batteries, work together to power hybrid electric cars. The battery of a hybrid electric car cannot be charged by plugging it in. Instead, the internal combustion engine and regenerative braking are used to charge the battery. A smaller engine might be possible thanks to the electric motor’s added power. Additionally, the battery can reduce engine idling while stopped and power auxiliary loads. These features work together to improve fuel efficiency without compromising performance. Raise your knowledge of hybrid electric automobiles.
Key Auxiliary Components of a Hybrid Electric Vehicle Battery: In an electric drive vehicle, the low-voltage auxiliary battery operates the car’s accessories as well as starting the engine before the traction battery kicks in.
This device, known as a DC/DC converter, transforms higher-voltage DC power from the traction battery pack into the lower-voltage DC power required to operate the vehicle’s accessories and recharge the auxiliary battery.
Electric Vehicle generator: Produces power during braking by harnessing the motion of the wheels, then feeds that energy back into the traction battery pack. Some automobiles employ motor generators that serve as both drives and regenerators.
Electric traction motor: This motor powers the wheels of the vehicle by drawing energy from the traction battery pack. Some automobiles employ motor generators that serve as both drives and regenerators.
Exhaust system: The exhaust system distributes the engine’s exhaust gases out the tailpipe. A three-way catalyst is intended to lower engine-out emissions in the exhaust system.
Fuel filler: A nozzle from a fuel dispenser connects to the vehicle’s receptacle to fill the tank.
The fuel tank (gasoline) stores gasoline on board the vehicle until it is required by the engine.

2 thoughts on “Hybrid Electric Vehicle”